Shaping the future of technology through ITEA innovations
The successes and impact of ITEA across sectors
For more than 25 years, ITEA has been fostering software innovation, enabling projects to deliver groundbreaking impact and shape the future of technology. Through almost 50 editions of the ITEA Magazine, the Success stories have been the proof of how ITEA projects have reshaped sectors such as healthcare, cybersecurity, automotive, and industry. We are very proud to look back on the incredible impact that ITEA projects have made over the past decades and are pleased to share some trends and highlights with you!
Revolutionising software development

One of the greatest achievements of ITEA projects has been the transformation of how software is developed, tested, and deployed. In its early years, several ITEA projects focused on tackling the increasing complexity of software through standardised architectures and middleware solutions. Projects laid the groundwork for interoperability between systems, streamlining development and enhancing software portability.
The ITEA project EAST-EEA ran from 2001-2004 and paved the way to the automotive industry's standardised platform for automotive applications: the Automotive Open Systems Architecture (AUTOSAR). AUTOSAR is now a global industrial initiative that brings together about 250 original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), Tier 1 automotive suppliers, software suppliers, semiconductor manufacturers, tool suppliers and others worldwide.
In addition, software testing has seen major improvements, thanks to enhanced test automation and streamlined verification processes, and ITEA has also played a key role in accelerating software generation, producing software up to 90% faster than human-written alternatives.
The emphasis in ITEA projects has now shifted towards AI-driven automation, low-code development, and collaborative platforms and the industry is moving towards fully autonomous software systems capable of self-correction and enhancement.

Transforming healthcare

Over the years, healthcare technology has undergone a major transformation thanks to ITEA projects, moving from enhanced medical imaging to real-time, AI-driven decision-making. Early advancements of the projects focused on integrating imaging systems into clinical workflows, improving diagnostics, and enabling minimally invasive procedures. This laid the groundwork for better patient outcomes through more precise interventions.
With the rise of digital health, attention shifted to remote monitoring and patient-centred care. Wearable devices and smart applications began providing real-time health data, improving chronic disease management and enabling early detection of complications. At the same time, interoperability between medical systems became a priority, ensuring seamless data exchange between different healthcare providers and reducing inefficiencies in patient care.
Advancements in AI and real-time analytics further revolutionised treatment strategies. High-speed imaging, predictive analytics, and real-time tracking of organ movement during procedures enhanced the accuracy of treatments like radiation therapy, reducing side effects and improving patient recovery.
As a result of the STARLIT project, the number of radiotherapy treatments needed for cancer patients will be reduced and so too will the related burden. A cancer patient can also benefit from a risk reduction of side effects as less tissue is damaged. This improves the overall safety of the treatment and reduces recovery time.
Most recently, AI-driven automation and predictive modelling have enabled proactive healthcare, where treatments are optimised in real-time based on patient-specific data. The shift from traditional care models to fully connected, intelligent healthcare ecosystems is redefining medicine, making treatments more precise, reducing costs, and significantly improving patient quality of life.
Driving energy efficiency and sustainability
With rising energy demands and climate concerns, ITEA projects have contributed to smarter, more sustainable energy solutions. At the start of the ITEA Magazine, we could see a focus on integrating renewable energy sources and optimising industrial power consumption. Since then, digital twins and AI-driven energy management systems have taken centre stage, offering real-time energy forecasting and cost reductions.
The SPEAR project allows for a greater uptake of renewable energies (such as solar and wind) which were previously difficult to optimise on a large scale due to their weather dependency. This gives SPEAR a vital role in reducing CO2 emissions and slowing the speed of climate change throughout society as a whole. Through the smart selection of energy sources, the smart adaptation of process-relevant parameters, and the reduction of power peaks, energy costs have been reduced by roughly 10%.
Strengthening cyber security and protecting critical infrastructures

Safety and security technologies developed through ITEA have also evolved significantly, adapting to an increasingly connected and digital world. Initially, efforts focused on strengthening cybersecurity for critical systems, ensuring that software vulnerabilities could be detected and mitigated before they caused harm.
As digital infrastructure expanded, surveillance systems were enhanced through multi-modal sensors and threat assessment models to improve situational awareness in security-sensitive domains such as coastguard operations. These advancements also extended to automotive safety, where new model-based development processes were introduced to comply with evolving safety standards, improving functional safety in vehicles.
SAFE was a crucial piece of the puzzle in establishing ISO 26262, a worldwide standard and one of the most important in the automotive industry. Thanks to the SAFE project, Continental established the ISO 26262 compliance in two major domains, namely the safety critical domains of powertrains and chassis brake systems. These domains represent 40% of Continental's product share and, thanks to the SAFE project, Continental was able to keep its leading role in these domains.
With the rise of IoT and cloud-based solutions, security challenges shifted towards identity and access management, real-time threat response, and automated countermeasure enforcement. AI-powered solutions enabled faster detection and mitigation of cyberattacks, reducing response times from hours to minutes and minimising financial losses.
Championing standards and interoperability
One of ITEA's unique strengths is its ability to develop technological standards that enable seamless collaboration across industries. Standardisation efforts began with ensuring software and hardware compatibility across platforms. Over time, ITEA has championed industry-wide frameworks, facilitating collaboration and efficiency.
EPAS has paved the way to a series of universal ISO standardised specifications for European card payments free of royalty and charges. Ultimately, this has been extended worldwide with the endorsement of the EPAS specifications (CAPE) as a global ISO 20022 message standard. ISO 20022 is today 'the' reference in standardisation in finance. Instant payment solutions are being developed today based on ISO 20022 credit transfer standards which may, in the future, facilitate the development of hybrid card and credit transfer payment solutions.
The objectives of the MODELISAR project were to boost collaboration and innovation across system and software disciplines and to test the vehicle behaviour earlier, faster and more affordably in the virtual world. During the project, an international and open Functional Mock-up Interface (FMI) standard was developed to conveniently exchange and interoperate models from different modelling and simulation environments.
The main and most sustainable project outcome of ACOSAR, the Distributed Co-simulation Protocol (DCP), has been developed as a Modelica Association Project (MAP) and is available as an open-access international standard.
Building smart, connected cities

ITEA's impact also extends into smart cities e.g. by bringing urban planners and citizens together on a collaborative platform and combining BIM and GIS technologies for better collaboration in urban planning, enhancing the co-creation of smarter cities. And thanks to the development of digital twin technology for public safety, cities can predict and respond to emergencies more effectively.
A city representative responsible for video surveillance can now work with one single screen and, once logged in, take a virtual walk through a 3D model of the city and see everything that is happening in a single view. This facilitates his/her work much better compared to the previous situation where (s)he needed to monitor up to 60 live screens in the control room and handle dozens of calls during the day from local citizens and officers regarding suspicious events. (ITEA project PS-CRIMSON
Industry 4.0 and the future of manufacturing
Over the years, industrial technology has undergone a significant transformation, evolving from early digital simulations to automated, AI-driven systems. Initially, the focus was on improving efficiency through virtual testing and simulation, enabling manufacturers to optimise production lines before physical implementation. As the industry progressed, the challenge shifted to integrating different engineering tools and software. A breakthrough came with the development of universal standards for data exchange, allowing seamless communication between various design and simulation platforms.
The VMAP project has created the world's first CAE workflow interface standard for integrating multi-disciplinary and multi-software simulation processes in the manufacturing industry. This standard is vendor-neutral, cost-free and completely open. The first public version of the standard was announced by the VMAP project in January 2020, before the end of the project.
With greater connectivity, the next step was enabling real-time communication between machines in manufacturing environments and, most recently, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning has brought a new level of autonomy. Predictive and prescriptive maintenance systems now analyse real-time data to anticipate failures, optimise performance, and reduce downtime.
Within PIANiSM, B3 Systems developed customised algorithms that not only predict equipment failures but also prescribe preventive measures, thereby reducing downtime and maintenance costs. This capability has enabled manufacturers to transition from traditional, reactive maintenance strategies to proactive, predictive approaches. For instance, clients have reported a reduction in unplanned downtime by up to 40% and maintenance cost savings of 20-30%, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and productivity.
Accelerating automotive and transportation innovation

In the automotive domain, early efforts of ITEA projects focused on integrating software and hardware interoperability within vehicles, enabling seamless communication between electronic control units (ECUs).
As vehicles became more complex, model-based system design and simulation tools were introduced to enhance collaboration across engineering disciplines. These innovations allowed manufacturers to test and validate vehicle behaviour in virtual environments, accelerating development cycles and improving safety. Multi-core processing and real-time analysis also became critical, enabling high-performance computing for autonomous driving and advanced driver-assistance systems.
With the rise of connectivity, the focus shifted to secure, open vehicle-to-cloud platforms that support real-time data exchange between vehicles, infrastructure, and the cloud. Standardised interfaces and open-source ecosystems were developed to break down proprietary barriers, fostering innovation in mobility services, predictive maintenance, and traffic optimisation.
n November 2019, APPSTACLE has launched the first release of the Eclipse KUKSA platform that unifies the technologies across the vehicle, IoT, cloud and security domains to provide an open-source ecosystem to developers which addresses the challenges of the electrified and connected vehicle era. KUKSA shows large companies that there is more to be gained from sharing data than from protecting it within proprietary solutions. As more vehicles become connected, more applications and services will emerge. Companies can therefore enhance the business domain while increasing the size of their own share.
Looking ahead: The future of ITEA
As we celebrate the 50th edition of ITEA Magazine, we also look forward to the future. ITEA will continue to drive innovation, support groundbreaking projects, and ensure that industries involved in ITEA remain competitive in an ever-changing technological landscape. Independent of the domain, from software development to cybersecurity and healthcare to energy efficiency, ITEA remains dedicated to shaping the future of technology, making the world a smarter, safer, more sustainable and happier place for generations to come.
Other chapters
Use the arrows to view more chapters

Editorial
By Dirk Elias and Régis Cazenave

50 up!
Reflections on the ITEA Magazine with former ITEA Chairman Rudolf Haggenmüller
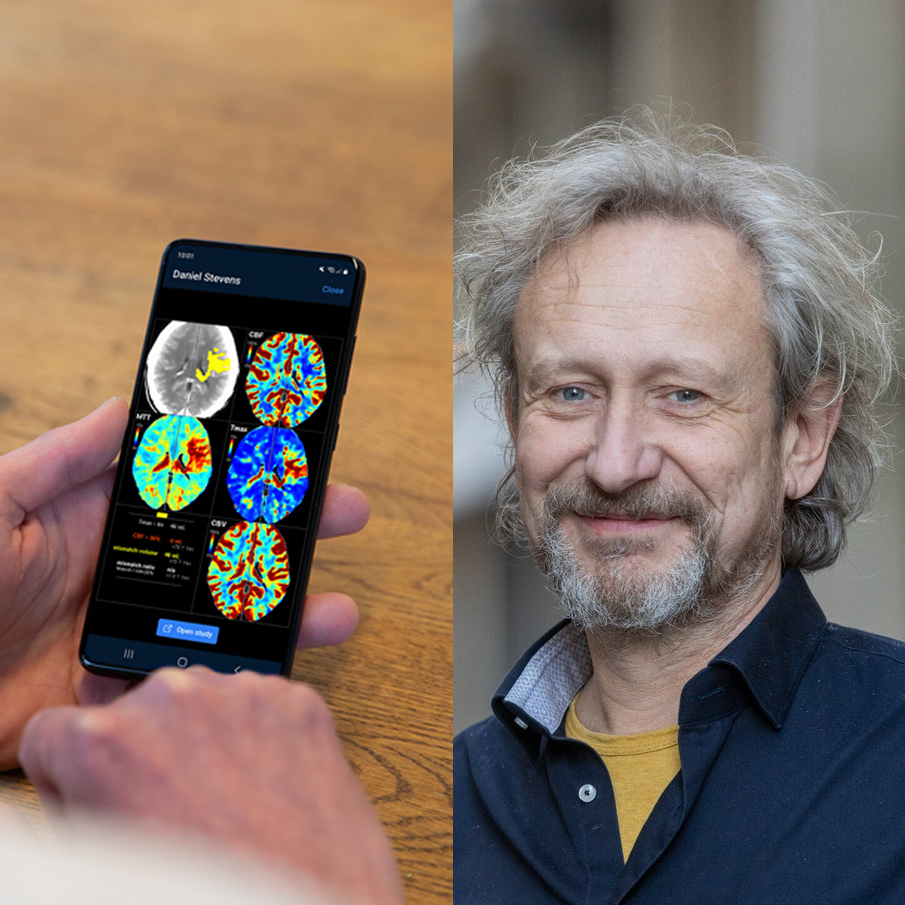
The transition towards data-informed healthcare
By Henk Marquering

Shaping the future of technology through ITEA innovations
The successes and impact of ITEA across sectors

Focus on ITEA’s Country focus
50 editions of collaboration and innovation across borders

Growth and change in the Community
Insights from long-standing members

ITEA communication goes fully digital
Stay connected with the Community and subscribe now!



